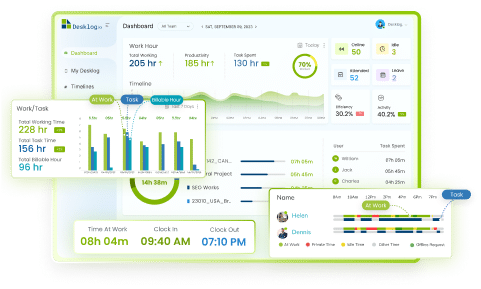
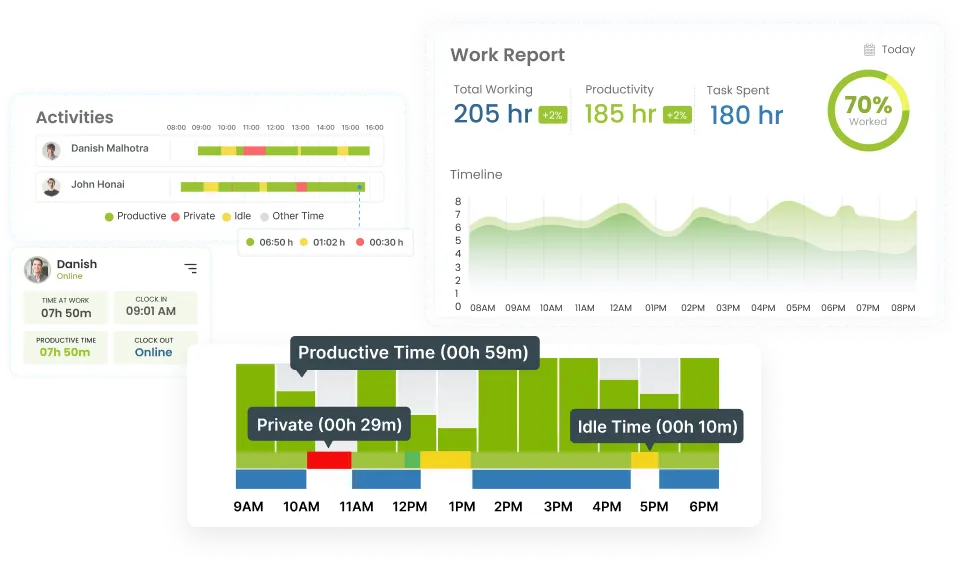
Absenteeism in the workplace can be a significant challenge, affecting not only an employee’s workload but also the team’s productivity and overall business profitability. Whether an employee is absent for a day or a week, the impact ripples through the organization. Identifying the root causes of absenteeism allows employers to offer necessary support and develop effective plans to improve employee performance.
While occasional absences for personal matters are expected, frequent absenteeism can signal deeper issues within the organization that need addressing to prevent negative effects on employee productivity. Research shows that only a small percentage of employers fully understand the reasons behind their employees’ absences, but by identifying these causes, absenteeism can be better managed, controlled, and reduced.
When comparing absentee days to the total number of working days in a month, the number of absences should ideally be kept to a minimum. To achieve this, it’s essential to understand absenteeism, its causes, and how to manage it proactively. An effective attendance management system helps track absenteeism, identify patterns, and enable proactive steps to reduce absences and address root causes.
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of absenteeism, offering valuable insights that can serve as a guide for effectively addressing and reducing absences in the future.
What’s Meant By Employee Absenteeism?
Employee absenteeism refers to the habitual or frequent absence of an employee from work, typically without valid or acceptable reasons. It can also encompass employees being away from work due to illness, personal reasons, or other unavoidable circumstances. Regular absenteeism can disrupt operations, affect team dynamics, and lead to increased costs for a company.
Authorized vs. Unauthorized Absences
Authorized Absences
These are absences that have been approved by the employer, usually in advance, or under circumstances that the employer recognizes as legitimate. Employees typically need to follow company procedures for notifying their manager, such as submitting a leave request or providing appropriate documentation. Examples include:
-
Sick leave (with a doctor’s note, if required)
-
Vacation leave
-
Maternity/paternity leave
-
Jury duty leave
-
Bereavement leave
What Qualifies As Authorized Leave?
Authorized leave is any type of absence that is pre-approved by the employer and falls within the bounds of company policies. This can include:
-
Sick leave (when an employee is unable to work due to health reasons)
-
Vacation days (personal time off that has been requested and approved)
-
Emergency leave (in cases such as a death in the family or a sudden emergency)
-
Parental leave (time taken for maternity, paternity, or adoption purposes)
-
Public holidays (if the company observes them)
Employers typically require notice in advance for planned leaves and may request supporting documents for certain types of authorized leave (e.g., doctor’s note for illness).
Unauthorized Absences
These are absences where the employee fails to obtain prior approval or provide a valid reason for being absent from work. These can disrupt operations and are often considered a breach of company policy. Examples include:
-
Not showing up without notice
-
Taking extended breaks without approval
-
Absent without a valid reason or documentation
Examples of Unauthorized Absences

Failure to show up without prior notice (e.g., an employee doesn’t inform the employer that they will be absent)

Frequent short-term absences without reason or prior approval (e.g., calling in sick repeatedly without proper documentation)

Skipping work without informing the supervisor or without any valid reason for not being at work

Excessive tardiness where the employee does not show up at the scheduled time and doesn’t provide a valid reason.
Planned vs. Unplanned Absences
Planned Absences
These are absences that an employee and employer anticipate in advance. The employee usually requests this time off well before the absence occurs, giving the employer enough time to adjust workloads and plan for coverage. Examples of planned absences include:
-
Vacation days
-
Scheduled medical treatments
-
Appointments
-
Personal leave or holidays
Unplanned Absences
These are absences that occur unexpectedly, often because of illness, personal emergencies, or other unforeseen circumstances. Unplanned absences are harder to manage because they usually require immediate adjustments and can cause disruptions in workflow. Examples include:
-
Sudden illness
-
Family emergency
-
Accident or injury
How To Manage Both Types Effectively?

Planned Absences: These can be managed proactively. Employers can ensure sufficient staffing, redistribute work, or allow others to cover shifts. The key is to have a transparent system for requesting and approving time off and to plan well in advance.

Unplanned Absences: These require more flexibility and a rapid response. Employers might implement a contingency plan that involves cross-training employees so that others can fill in when someone is unexpectedly absent. It’s also beneficial for employees to have a clear process for notifying their employer about unplanned absences, as soon as they know they will be absent.
The Importance of Addressing Absenteeism
Impact on Productivity
Workflow and Deadlines

Disrupting Communication and Coordination: Absenteeism can also impact communication channels within a team. When an employee is absent, especially without prior notice, it can create gaps in communication, leaving team members uncertain about their responsibilities or missing vital updates.

Project Delays and Dependencies: In projects that involve multiple teams or departments, absenteeism can lead to bottlenecks. Certain tasks may be dependent on the completion of work by absent employees, causing a ripple effect of delays throughout the project timeline.
Team Morale

Loss of Leadership and Guidance: When managers or key team members are frequently absent, it can undermine their ability to lead effectively, leaving teams without proper direction or support. This can lead to confusion, frustration, and a sense of instability.

Employee Engagement: Persistent absenteeism can create a lack of accountability and foster a culture of disengagement. Employees may feel that absenteeism is being tolerated, which lowers their own commitment to being present and productive.
Long-Term Impact on Company Efficiency
Reduced Collaboration

Fragmented Work Output: With increased absenteeism, teams may struggle to stay cohesive. This can result in fragmented work output and missed opportunities for brainstorming or innovative solutions. Collaboration can be hindered when key people are unavailable to contribute ideas or expertise.

Impact on Cross-Departmental Cooperation: In large organizations, absenteeism might also hinder cross-functional cooperation. When employees from various departments are missing, it disrupts the flow of collaborative efforts and can impact larger strategic initiatives.
Quality of Work

Risk of Errors or Incomplete Work: Fewer employees on the job can lead to overburdened workers rushing to complete tasks, increasing the likelihood of errors or incomplete work. This can affect the company’s reputation for delivering high-quality products or services.
Financial Implications
Costs Associated with Absenteeism

Increased Recruitment and Training Costs: Companies that face chronic absenteeism may need to regularly recruit temporary or permanent employees to fill gaps. The cost of recruitment, hiring, and training new employees adds to the financial burden.

Overtime Expenses: To compensate for absenteeism, businesses may offer overtime to remaining employees. While this can help meet immediate needs, prolonged overtime can lead to employee burnout and increased labor costs.
Revenue Loss Due to Workforce Disruptions

Lower Customer Satisfaction: Absenteeism in customer-facing roles can lead to delays in service or lower customer satisfaction. Unfilled positions can result in slower response times, unmet customer needs, and a decline in service quality, which ultimately impacts revenue.

Decline in Sales or Production: In manufacturing or sales-driven environments, absenteeism directly reduces output, whether in the form of product units, client meetings, or sales conversions. Lower productivity due to absenteeism impacts the company’s ability to achieve sales targets and production goals, contributing to reduced revenue.
Effects on Team Morale
Impact on Team Collaboration

Fragmented Workload Distribution: When one employee is absent, the remaining team members often have to shoulder the workload, the workload distribution leads to a higher risk of task mismanagement, confusion, and redundancy in efforts. Over time, this can lead to a lack of enthusiasm and more frequent employee absenteeism.

Erosion of Trust and Communication: Teams that experience frequent absenteeism may start to lose trust in each other, leading to poor communication. As trust deteriorates, collaboration becomes strained, which further exacerbates absenteeism and low morale.
Employee Dissatisfaction and Workplace Stress

Pressure to Cover for Others: Employees who must take on the responsibilities of absent coworkers can become resentful if they feel overburdened. This feeling of being “taken advantage of” can lead to disengagement, stress, and burnout, perpetuating employee absenteeism.

Low Job Satisfaction: A lack of work-life balance, personal or family pressures, and stress related to increased workloads can contribute to employee dissatisfaction. Over time, dissatisfaction with the workplace can lead to higher turnover rates and a general decline in employee retention.
Underlying Causes of Absenteeism
Poor Management and Leadership

Lack of Clear Expectations: If employees are unclear about expectations or feel unsupported by their managers, they may be more likely to disengage or take frequent time off. Employees need clear communication about goals, performance expectations, and the consequences of employee absenteeism.

Inadequate Problem-Solving by Management: Absenteeism may be indicative of larger problems within the organization, such as inefficient management practices or poor work culture. If these issues are not addressed, employee absenteeism may continue or even worsen over time.
Lack of Motivation and Engagement

Disconnect Between Employee and Organization: Employees who feel disconnected from the company’s mission, values, or vision are more likely to take unauthorized absences or exhibit disengagement behaviors. Low engagement typically correlates with higher absenteeism rates.

Poor Job Fit or Career Development Opportunities: Employees who feel they are in the wrong role, or who do not see a clear career path, may be more inclined to take time off or disengage. Lack of career development opportunities can contribute to absenteeism, as employees may feel there’s no incentive to be present.
Addressing Absenteeism Proactively
Implementing Flexible Work Options

Remote or Hybrid Work: Offering flexible schedules or the option to work remotely can help employees balance their personal and professional lives, potentially reducing employee absenteeism related to family responsibilities or personal health issues.

Compressed Work Weeks or Job Sharing: For employees facing personal issues, offering flexible arrangements such as compressed workweeks (e.g., four 10-hour days) or job sharing can help them manage time off without negatively impacting productivity.
Proactive Attendance Policies

Clear and Fair Attendance Policies: Establishing clear policies for attendance, including acceptable leave, how absences are recorded, and the consequences of excessive employee absenteeism, can encourage employees to be more responsible about their attendance.

Return-to-Work Interviews: After an employee returns from a significant absence, conducting a return-to-work interview can help identify the cause of the absence and provide an opportunity to address any underlying issues. This shows employees that the company cares about their well-being and is invested in their success.
Employee Wellbeing and Support

Offer Health and Wellness Programs: Proactively addressing employee health (both mental and physical) can reduce employee absenteeism caused by personal illness or stress. Programs like fitness memberships, stress management workshops, or even on-site healthcare can be highly beneficial.

Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Offering confidential counseling services can help employees manage personal or mental health issues, thereby preventing employee absenteeism related to burnout or stress.
In summary, absenteeism whether authorized or unauthorized, planned or unplanned has significant implications for productivity, financial health, and overall team morale. Addressing absenteeism proactively and equitably is essential for maintaining a positive and efficient work environment.
Common Causes of Employee Absenteeism
Employee absenteeism can stem from various factors, each affecting employees in different ways. Let’s break down each of these causes and discuss them in more detail, as well as find strategies employers can use to mitigate them:
Health-Related Issues
Physical Health
Chronic Illnesses and Workplace Injuries: Employees with long-term conditions, such as diabetes, heart disease, or conditions requiring ongoing treatment (e.g., cancer), may experience frequent absenteeism due to medical appointments, treatment sessions, or flare-ups. Workplace injuries, whether acute or long-term, can lead to significant time off for recovery.
Short-Term Illnesses: Common illnesses such as colds, flu, or digestive issues can result in short-term absenteeism. While generally temporary, these illnesses can disrupt work schedules, especially in larger teams where one absence might have a more noticeable impact.
Employer Strategies:

Health Support Programs: Provide medical insurance, wellness programs, and onsite clinics.

Flexible Work Options: Allow for telecommuting or flexible hours for employees who may need to attend medical appointments or recuperate at home.
Mental Health
Anxiety, Depression, and Workplace Burnout: Mental health issues have become increasingly prevalent in the workplace. Anxiety and depression can affect an employee’s ability to focus, communicate effectively, and perform tasks. Burnout, caused by chronic stress and unrealistic work expectations, can lead to emotional exhaustion and absenteeism.
Impact of Mental Health Awareness: Many organizations are now recognizing the importance of mental health and offering mental health days, counseling services, and stress management programs. This helps to reduce employee absenteeism by addressing the root causes.
Employer Strategies:

Mental Health Days & Programs: Employers can offer mental health days and integrate employee assistance programs (EAPs) to provide counseling and support.

Training for Managers: Encourage management to recognize mental health issues early on and create an open, supportive environment where employees feel safe to discuss challenges.
Workplace Environment
Bullying and Harassment
Toxic Work Culture: Workplace bullying, harassment, and discrimination can significantly impact employee wellbeing. These factors create an atmosphere of fear, low morale, and disengagement, often leading to employee absenteeism as employees seek to avoid the stress and anxiety associated with the workplace. Additionally, a culture of toxic productivity can exacerbate these issues, pushing employees to overwork in unhealthy ways, which ultimately contributes to burnout and higher absenteeism.
Creating a Safe and Inclusive Work Environment: A safe environment fosters trust, collaboration, and engagement, reducing employee absenteeism. Organizations should have clear anti-bullying policies and provide training for all employees on respectful behavior.
Employer Strategies:

Strict Policies Against Bullying and Harassment: Implement and enforce anti-harassment policies, ensure there are clear reporting channels, and take swift action when issues arise.

Inclusivity Training: Regular training on diversity and inclusion can help employees feel respected and valued.
Job Satisfaction
Workplace Culture: A positive organizational culture can lead to higher engagement, employee satisfaction, and fewer absenteeism issues. Conversely, poor culture, unclear expectations, and lack of appreciation contribute to dissatisfaction, leading employees to disengage or take more time off.
Low Engagement and Lack of Motivation: Employees who don’t feel valued or motivated are more likely to be absent. When they don’t see the purpose or value in their work, they may not feel committed to showing up consistently.
Employer Strategies:

Recognition and Rewards Programs: Foster a culture of recognition where employees are acknowledged for their contributions.

Provide Career Development Opportunities: When employees can grow within the company, they are more likely to be motivated and engaged.
Personal and Family Responsibilities
Family Emergencies and Caregiving Duties
Family Emergencies: Employees may need time off unexpectedly to address family emergencies, such as the illness of a loved one or the death of a family member.
Caregiving Duties: For employees with caregiving responsibilities (such as caring for children or elderly relatives), balancing work and personal life can be challenging, leading to frequent employee absenteeism.
Employer Strategies

Paid Family Leave: Offer flexible leave policies that allow employees to manage family emergencies without the stress of unpaid leave.

Childcare and Elder Care Assistance Provide resources or subsidies for employees who need assistance with childcare or elder care.
Stress and Burnout
Overwork and Excessive Job Demands
Excessive Job Demands: Overwork and unrealistic job demands are among the most significant causes of employee absenteeism. If employees are expected to consistently work long hours without relief, it can lead to chronic stress, burnout, and eventual absenteeism.
Employer Strategies

Workload Management: Ensure workloads are balanced and that employees are not overwhelmed. Regularly check in with employees to ensure they are managing their responsibilities effectively.

Encourage Breaks and Time Off: Promote a culture that encourages employees to take regular breaks and time off to recharge.
Burnout and Disengagement
Burnout causes emotional exhaustion and physical fatigue, leading to a drop in job performance and employee disengagement. Over time, this can result in an employee avoiding work altogether.
Employer Strategies

Mental Health and Wellness Initiatives: Offer regular programs that promote work-life balance, stress management, and overall wellness.

Regular Employee Feedback: Engage in open communication with employees to identify potential burnout signs early, offering support and solutions before issues escalate.
Substance Abuse
Employees struggling with substance abuse may frequently miss work due to their addiction or the physical and emotional toll it takes on their health. Substance abuse can also affect work performance, making it difficult for employees to focus, meet deadlines, or behave appropriately in the workplace.
Employer Strategies

Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs): Provide confidential counseling and support services to employees struggling with addiction. These services can offer treatment options, support groups, and advice on rehabilitation.

Substance Abuse Awareness Training: Educate managers and employees on the signs of substance abuse and provide a non-judgmental atmosphere for employees to seek help.
Measuring and Analyzing Absenteeism
Key Metrics and KPIs
Absenteeism Rate Formula:
Absenteeism Rate = (Total Absent Days/Total Available Work Days) × 100
This formula calculates the percentage of workdays missed and helps in identifying overall absenteeism trends.
Key Indicators to Monitor

Frequency and Duration of Absences: Track how often and how long employees are absent. A high frequency of short-term absences may indicate different issues than a pattern of long-term absences.

Patterns of Employee Absenteeism: Look for trends such as absences on specific days of the week (e.g., Mondays or Fridays) or during certain seasons (e.g., flu season or holidays).

Planned vs. Unplanned Absences: Differentiating between planned absences (e.g., vacations) and unplanned ones (e.g., sickness) helps identify potential areas of concern.
Tools and Techniques for Tracking
Manual vs. Automated Tracking
Manual Tracking
-
While cost-effective, manual methods (like spreadsheets or paper records) are prone to human error and can be time-consuming. Additionally, incorporating web timer into these processes can help track time spent on specific tasks, but even they are not immune to inconsistencies or disruptions, such as inaccurate manual entries or technical glitches. Over time, these issues can compound, leading to inefficiencies and unreliable data. Automated systems or digital tools can help eliminate these risks and simplify operations.
Automated Tracking
-
Automated systems using tools like biometric scanners or time-tracking softwares like Desklog, offer accuracy, real-time tracking , and easy data access, improving efficiency.
Automated Tracking with Desklog: Increasing Efficiency, Productivity & Focus
Desklog offers automated tracking, ensuring accuracy and real-time tracking of employee activity. This automated system provides easy access to data, increasing efficiency and enabling businesses to manage time more effectively.
Desklog offers automated time tracking, ensuring accuracy and real-time tracking of employee activity. This system not only provides easy access to data, increasing efficiency and enabling businesses to manage time more effectively, but it also promotes focus time by minimizing distractions.
By giving employees the tools to manage their time efficiently, Desklog supports a better work-life balance, helping them stay on track while also prioritizing employee well-being.
With insights into individual work patterns, businesses can foster a healthier, more productive work environment, encouraging breaks and downtime when needed.
Key Features of Desklog
-
Attendance Management: Desklog tracks employee attendance, providing accurate records and reducing absenteeism by identifying patterns and trends, helping you take proactive measures.
-
Shift Scheduling: The shift management system allows for efficient planning and assignment of work shifts, ensuring adequate coverage and optimal staffing levels to meet operational demands.
-
Clock-in/Clock-out: Employees can record their work start and end times with Desklog’s clock-in/clock-out feature, ensuring accurate tracking of hours worked and maintaining precise attendance data.
Interpreting Absenteeism Data
Identifying Trends and Root Causes
-
Look for seasonal trends or specific patterns, such as frequent absences in certain departments or individuals. This could indicate issues such as health problems, work-related stress, or low engagement.
-
Identify if absenteeism is linked to employee demographics (e.g., age, tenure) or work-related factors (e.g., job dissatisfaction, overwork).
Using Data to Implement Proactive Measures
-
Targeted Interventions: If employee absenteeism is concentrated in certain departments or teams, take targeted actions to address potential causes, such as workload adjustments or better management practices.
-
Wellness Programs: If health-related absences are high, introduce wellness initiatives like fitness programs, stress management, or mental health support.
-
Flexible Work Options: For employees facing personal challenges, offering flexible work hours, remote options, or caregiving support can help reduce absenteeism.
-
Recognition Programs: Recognize employees for their hard work to increase engagement, morale, and overall attendance.
By consistently measuring and analyzing employee absenteeism, employers can uncover patterns, address the root causes, and implement targeted strategies to reduce absenteeism. Using HR software, monitoring key metrics, and taking proactive steps can ultimately enhance employee engagement, improve morale, and increase productivity.
Strategies to Mitigate and Prevent Absenteeism
Developing a Clear Attendance Policy
Crafting Effective Attendance Guidelines
-
Develop a clear, written attendance policy that outlines expectations for punctuality, acceptable absences, and the process for requesting leave. The policy should also address how absenteeism is tracked and the consequences for excessive absenteeism.
Communicating Policies to Employees
-
Ensure all employees are aware of the policy. Communicate it through onboarding, employee handbooks, emails, and team meetings. Clear communication helps avoid confusion and sets expectations from the start.
Promoting Employee Well-being
Workplace Wellness Programs
-
Introduce wellness programs focusing on physical and mental health. Programs could include on-site fitness centers, mental health workshops, stress reduction sessions, and ergonomic workplace designs.
Health Benefits and Preventive Care Initiatives
-
Offer complete health benefits, including coverage for preventive care. Encourage employees to get regular check-ups and utilize mental health services through employee assistance programs (EAPs), reducing health-related absenteeism.
Enhancing Engagement and Job Satisfaction
Creating a Positive Work Culture
-
Foster an inclusive, supportive work environment where employees feel valued and engaged. A positive culture leads to higher job satisfaction, which in turn can reduce absenteeism due to disengagement.
Recognizing and Rewarding Employee Contributions
-
Implement recognition programs that reward consistent attendance, hard work, and contributions. Recognizing employees for their efforts helps improve morale and reduces absenteeism caused by lack of motivation.
Providing Flexible Work Arrangements
Remote Work, Hybrid Models, and Flex-Time Options
-
Offer flexible working options like remote work, hybrid models, and flexible hours to accommodate employees’ personal needs. Flexibility allows employees to better balance work and personal life, reducing absenteeism.
How Flexibility Reduces Absenteeism
-
Flexibility reduces the pressure employees may feel due to personal issues, such as childcare or family responsibilities, making them less likely to take unplanned leave. It also helps employees manage health issues more effectively.
Implementing Return-to-Work Programs
Strategies to Help Employees Reinstate
-
After an extended leave, provide structured return-to-work programs that offer a gradual transition back into full-time work. This can include flexible hours, reduced workloads initially, or job modifications to accommodate the employee’s needs.
Managing Post-Leave Transitions Effectively
-
Ensure employees have proper support when returning from leave (whether for medical reasons, personal reasons, or vacation). Check in with employees to ensure they feel supported and confident in reintegrating into the workplace.
HR Best Practices in Managing Absenteeism

Encouraging Open Dialogue About Attendance Issues
Creating an open and trusting environment where employees feel comfortable discussing attendance challenges helps address problems early. Encouraging regular check-ins and open conversations allows employees to be honest about personal or work-related issues, leading to more proactive solutions and a positive work culture.

Training Managers to Address Absenteeism Constructively
Managers should be trained to handle absenteeism with empathy and professionalism. Training should focus on recognizing absenteeism patterns and addressing underlying issues through constructive conversations, rather than punishment, to create a supportive work environment that fosters problem-solving.

Equipping Leadership to Handle Absenteeism Effectively
Leadership should be proactive in managing absenteeism by understanding its causes and using tools like data analytics to predict trends. By addressing issues early and setting a positive example, leaders can create an organizational culture that values good attendance and supports employees in managing absences.

Recognizing Warning Signs and Addressing Issues Early
Identifying early warning signs of absenteeism, such as frequent short-term absences or changes in performance, allows managers to intervene before issues escalate. Proactive discussions can uncover the root causes, enabling early solutions that prevent chronic absenteeism and support employee well-being.

Utilizing Absence Management Software:
Absence management software helps HR Departments track absenteeism, automate requests, and analyze trends. These tools improve efficiency, reduce errors, and allow organizations to address absenteeism proactively, leading to better decision-making and compliance with attendance policies.

Creating a Clear Attendance Policy
A well-defined attendance policy sets clear expectations and outlines consequences for absenteeism. Transparency ensures fairness and consistency, helping employees understand their responsibilities while providing a framework for managers to follow when managing attendance issues.

Offering Flexibility and Supportive Leave Programs
Offering flexible work schedules or remote work options helps employees manage personal responsibilities, reducing absenteeism. Supportive leave programs, like paid sick or family leave, also show employees that their personal needs are valued, leading to better attendance and engagement.

Promoting Employee Well-being and Engagement
Focusing on employee well-being through wellness programs and mental health support can reduce absenteeism. Engaged and healthy employees are less likely to take frequent sick days, as they feel supported in balancing work and personal life.

Incentivizing Good Attendance
Rewarding employees for consistent attendance, such as through recognition or bonuses, encourages a culture of responsibility. Positive reinforcement motivates employees to maintain good attendance habits and feel valued for their commitment to the organization.

Implementing Return-to-Work Programs
Return-to-work programs help employees ease back into their roles after an absence by offering modified duties or flexible hours. These programs support employees’ smooth transition back to work, reducing the likelihood of future absenteeism and demonstrating the organization’s commitment to employee well-being.
Case Studies: Successful Absenteeism Management
Mid Cheshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Mid Cheshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust reduced long-term sickness absence rates from 4.5% to 3.5% in 12 months by focusing on employee wellbeing. They implemented a training program to help managers manage long-term absences and introduced a new case management approach for better collaboration. Voluntary health assessments were offered to employees with ongoing health issues, aligning with research that highlights wellbeing as a key factor in reducing absenteeism.
iOSS
iOSS, a software company, successfully reduced its employee absenteeism rate by 20% through the implementation of their time-tracking software, Desklog. This software includes an attendance tracking feature that provides real-time tracking of employee work hours, allowing management to easily identify patterns of absenteeism.
According to Abdul Gafoor K V, Co-founder and Chief Operations Officer, the tool not only improved attendance but also promoted accountability and transparency among the team. By integrating this technology, iOSS was able to proactively address absenteeism issues, ensuring that managers could quickly intervene and support employees before absenteeism became a recurring problem. This data-driven approach helped foster a more disciplined work environment and contributed to overall improvements in employee engagement and productivity.
In Summary
Employee absenteeism is a significant concern for businesses, as it can lead to disruptions in productivity, team morale, and financial stability. By understanding the distinction between authorized and unauthorized absences, as well as the differences between planned and unplanned absences, employers can take proactive steps to manage absenteeism effectively.
Implementing clear attendance policies, promoting employee well-being through health programs, and fostering a supportive work environment can help reduce absenteeism rates.Moreover, addressing the underlying causes, such as physical and mental health issues, can help organizations create a more engaged and motivated workforce.
Ultimately, balancing flexibility with employee accountability is key to maintaining an efficient, productive, and positive work environment. By addressing absenteeism proactively, employers can safeguard both the immediate and long-term success of their teams and the company as a whole.
FAQ
1What is employee absenteeism?
Employee absenteeism refers to the habitual or frequent absence of an employee from work, typically without valid or acceptable reasons. It can be due to illness, personal issues, or other unforeseen circumstances but can disrupt operations and affect productivity.
2 What’s the difference between authorized and unauthorized absences?
Authorized absences are those approved by the employer, such as sick leave, vacation, or family leave, usually with prior notice. Unauthorized absences occur when employees don’t inform their employer or fail to provide a valid reason for their absence, leading to disruptions in the workplace.
3What are the three main components of RPM?
Employers can manage absenteeism by implementing clear attendance policies, offering flexible work options, and ensuring proactive communication. Planning for both planned and unplanned absences and cross-training employees for coverage can also help minimize disruptions.
4How does absenteeism impact team morale?
Absenteeism can strain team morale by increasing workloads for the remaining employees, creating feelings of frustration, and potentially leading to burnout. It can also erode trust and communication, affecting collaboration and overall job satisfaction.
5 What are the common causes of employee absenteeism?
Common causes include health issues (both physical and mental), poor management practices, lack of motivation or engagement, job dissatisfaction, and personal or family-related problems. Addressing these underlying causes is crucial for reducing absenteeism and improving employee well-being.
6 What are the common causes of employee absenteeism?
Common causes include health issues (physical and mental), workplace environment factors (like bullying or harassment), personal and family responsibilities (such as caregiving), stress and burnout from overwork, and substance abuse. These factors can lead to frequent or prolonged absences.
7 How can employers address absenteeism related to mental health?
Employers can offer mental health days, employee assistance programs (EAPs), and stress management workshops. Additionally, training managers to recognize mental health challenges and creating a supportive work environment can help reduce absenteeism caused by mental health issues.
8How does overwork contribute to absenteeism?
Excessive job demands and overwork can lead to stress, burnout, and physical fatigue. This can result in absenteeism as employees need time off to recover from emotional exhaustion and to prevent further health issues.
9What strategies can employers use to manage absenteeism effectively?
Employers can implement clear attendance policies, promote employee well-being with wellness programs, provide flexible work arrangements, offer return-to-work programs, and use data analytics to monitor absenteeism trends for proactive management.
10 How can flexible work arrangements reduce absenteeism?
Flexible work options, such as remote work or flexible hours, allow employees to better manage their personal responsibilities and health issues. This flexibility can reduce stress, improve work-life balance, and ultimately lead to fewer unplanned absences.