Desklog tracks productivity by considering your productive time by calculating time spent on productive & non-productive apps and URLs. To calculate productive time, Desklog categorizes apps and URLs as productive or non-productive.
When you are working on an App that contains URLs, only the URLs are considered in the calculation. If a user is on a productive app but visits a non-productive URL, it’s counted as non-productive time. However, using a non-productive app with a productive URL will count as productive time.
For example, if you classify Google Chrome as a productive app but visit Facebook, which is categorized as non-productive, the time spent on Facebook won’t be included in your productive hours, it’ll be added to your non-productive time. And the same goes the other way around. This way, we make sure your productivity tracking is both precise and professional.
- Productive Apps & URLs :
These are the apps & URLs that help you get your work done. Desklog recognizes when you’re using them and counts this as productive time.
- Non-Productive Apps & URLs:
These are the apps & URLs that might distract you from your work. Desklog notices when you visit them and doesn’t count this as productive time.
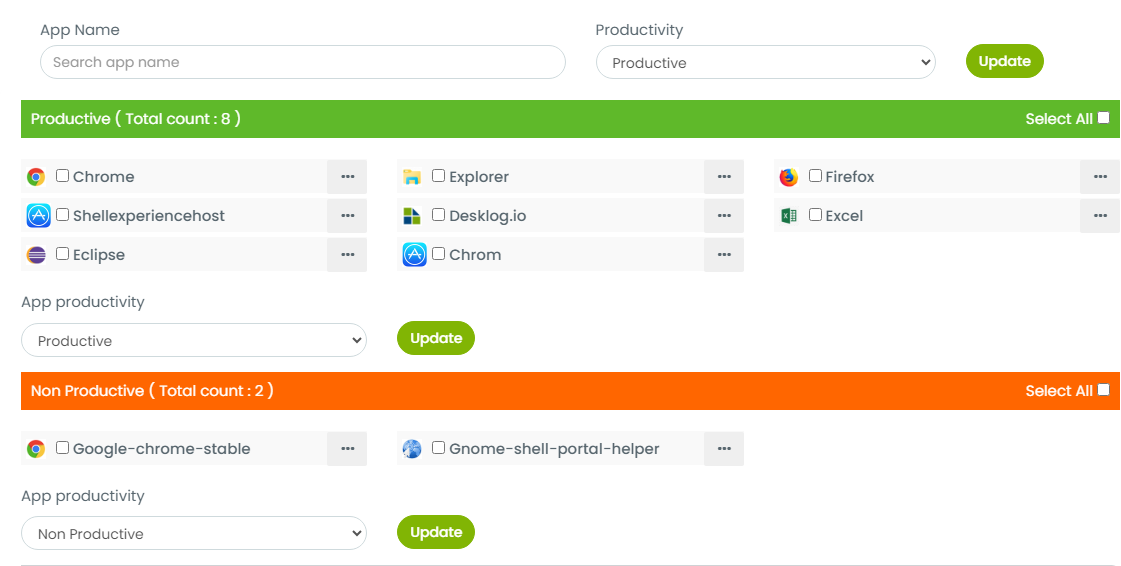
Classify Your Apps & URLs
To make sure Desklog gets it right, it’s important to categorize which apps and URLs are productive and non-productive. You can do this by classifying them from Desklog settings.